THC-O Acetate: The Psychedelic Cannabinoid
Get your space helmets ready!
We’re about to shed light on a (still) little-known compound: THC-O Acetate, otherwise known as Acetate THC X.
Estimated to be 300% more potent than Delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, you can probably understand why THC-O is fast gaining traction.
So, if you’re on the fence considering a THC O product, let’s get you fully acquainted with the science!

What Is THC-O Acetate: A New Age Cannabis Extract Experience?
Starter heads up:
There are plenty of scientific terms involved here. But we promise this won’t be a boring chemistry class. We’re here to learn what THC-O is vs. what it is not.
After all, we have the sacred right and responsibility to educate ourselves well. This way, we can make well-informed decisions as conscious cannabis consumers.
THC-O know-how is now in your control (prepare to get mind-blown). Here we GO!
- 20 gummies per pack
- Vegan & gluten free
- Free shipping
- $0.06 per milligram THCO (with discount code)
#1- THC-O Is A Man-Made Cannabinoid Derived From Hemp
THC-O is the shortened name for THC-O Acetate. Other names for this substance include ATHC and THC Acetate.
Yeah, plenty of words to describe the same compound. I know, it can get (slightly) confusing. More often than not, though, you’ll likely come across two briefer names:
- ATHC or
- THC-O
THC-O is the acetate version of Delta 9 THC. Most importantly, THC-O is not a naturally occurring cannabinoid.
Ganja plants produce almost 150 cannabinoids known up-to-date. These are termed phytocannabinoids.
Also, the human body produces its own cannabinoids known as endocannabinoids.
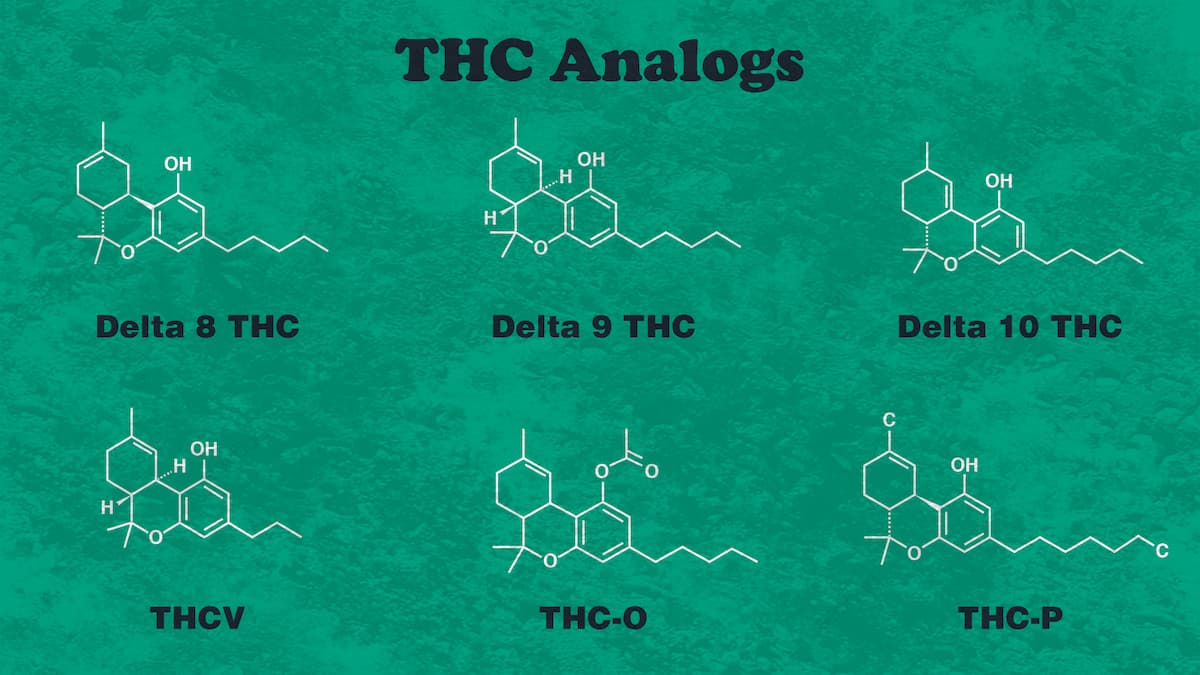
Some examples of phytocannabinoids include Delta 8 THC, Delta 9 THC, Delta 10 THC, THCP, CBD, and CBG, among others.
Related Read: THCO VS THCP
Usually, all phytocannabinoids are simply called cannabinoids. Hail to the brevity of the cannabis community culture! The very root “Phyto” stands for “of a plant,” “relating to plants.”
Phytocannabinoids like CBD occur in varying amounts. So ultimately, experts use different methods to collect and extract them.
But unlike CBD, THC-O is a manufactured cannabinoid. That’s why it doesn’t fall into the category of phytocannabinoids.
All cannabinoids, regardless of their origin, share the same important function.
At their very basic, they act on the endogenous cannabinoid system (aka ECS). The ECS is called our internal universal regulator as it maintains a balance between all other internal systems.
As we consume cannabis, phytocannabinoids act on the cannabinoid receptors in the ECS. Thus, we can experience the effects and therapeutic benefits of marijuana.
Related Reads: THC-O Carts, THC-O Wax, THC-O Gummies, THC-O Bud, THCO Tincture, THCO VS Delta 8
In Short Summary
While THC-O is not a naturally occurring cannabinoid, it does act on the endocannabinoid system.
#2 – THCA VS ATHC: Learn The Difference Easy
Okay, here we have a bit of a tricky word game. THCA and ATHC read quite similarly. It’s easy to get confused, right?
But in reality, there is a HUGE difference between THCA and ATHC.
THCA stands for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid. This is the parent molecule of THC, and it is not psychoactive.
Once subjected to heat, THCA converts into THC. The process of conversion is called decarboxylation.
If you’re a cannabis smoker, you regularly participate in this conversion. As you light up your joint, THCA turns into THC. Ta-da!
Here’s the major difference between THCA and ATHC:
With ATHC, “A” stands for “acetate.”
- Ultimately, THCA occurs naturally in cannabis plants.
- Contrary to that, ATHC can only be produced in a laboratory setting.
Notice that we use the term “produced.” ATHC is not extracted from cannabis. Instead, it must go through a complex chemical transformation process to occur.
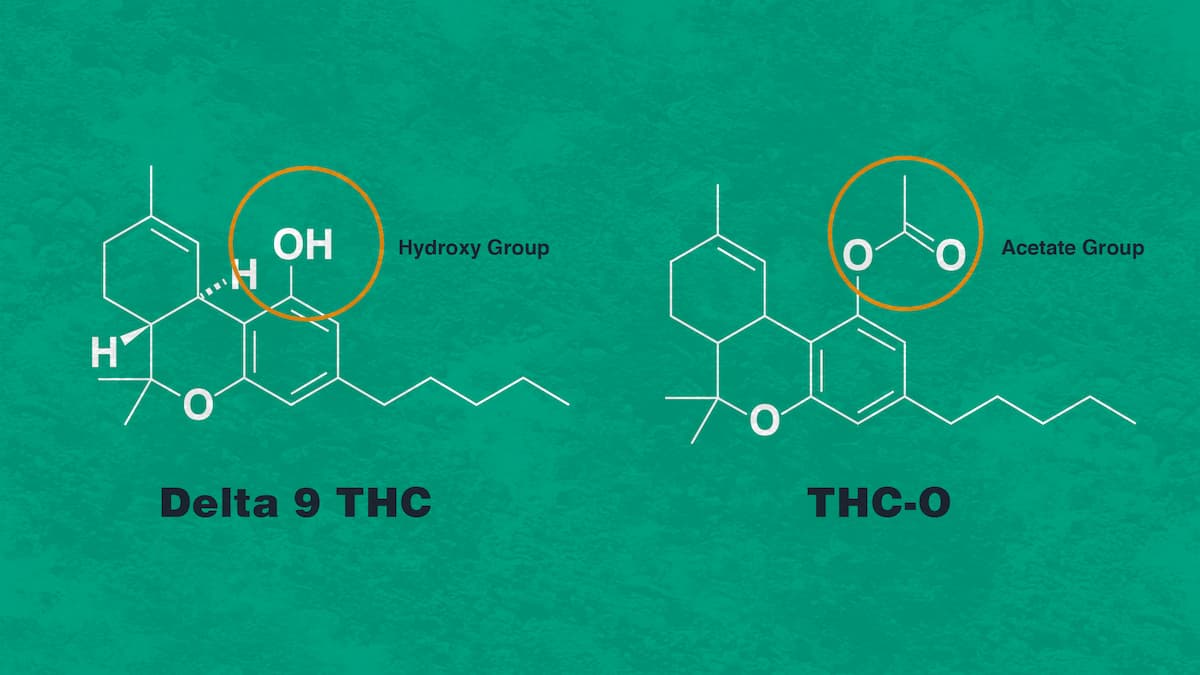
#3 – The Acetate Molecule Makes The THC Molecule Much Stronger
Okay, so the original, naturally occurring compound is THC. THC-O is an analog to THC.
Analog compounds have a similar structure to the original compound. Yet, an analog differs when it comes to a certain component.
In this case, THC-O and the regular THC molecule differ.
THC-O has an acetate molecule involved in its chemical structure.
Oh yes, the high potency secret is in the THC molecule. Or better said, in the acetate molecule. That’s what makes THC-O so much stronger than regular Delta 9 THC.
Think of THC-O as a manufactured product of Delta 9 THC conceived through a chemical process. Scientifically, this substance acts as a metabolic prodrug for Delta 9.
#4 – DIY THC-O: Mission Impossible
As a rule of thumb, you can’t whip up a batch of THC-O in the comfort of your home. Yup, it differs from some popular cannabis concentrates like THC Oil, where we may apply the DIY approach.
The tools and knowledge needed to produce THC-O are reserved for experts. However, it takes much more than picking up a handful of tools from the local store.
In labs, THC-O is produced using some quite volatile chemistry. The goal is to strip away all other chemical compounds, including terpenes and flavonoids.
Both terpenes and flavonoids have many science backed benefits. Yet, both of these are removed in order for THC-O to be born.
The final product is an odorless, tasteless (and hell yeah, POTENT) THC-O isolate.
#5 – THC-O VS. Whole-Plant Green Buds
So far, we have learned that it takes specific chemicals to acetylate THC and turn it into THC-O.
Since THC-O is an unnatural cannabinoid, which inevitably raises concerns among cannabis advocates (like me).
Certainly, whole-plant medicine offers invaluable benefits. But we must not turn our back around to the evolving science of cannabis.
New age ganja progress includes merging high technology and chemistry knowledge.
Compounds like THC-O may help in cases where a natural cannabinoid fails to provide the desired or needed effects. However, there is not much known about the short or long-term health effects of THC-O.
Remember, there are huge differences in human biology. Each person is unique, and hence, modern-day medicine and recreation have to focus on the element of uniqueness.
To stimulate cannabinoid receptors properly, some people may benefit better from a different version of cannabis’s compounds’ superpowers.
#6 – A Process In Progress: Brief History Of THC-O Acetate
Historically, the creation of the acetate version of Delta 9 THC has been a rather dangerous process. However, a qualified chemist can produce THC-O Acetate by using two chemicals: acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid.
From 1955 to 1975, a series of classified medical studies were conducted by the U.S. Army Chemical Corps. This involved THC Acetate in tests on dogs.
Research highlights that the acetate version can impair muscle function in dogs with twice the strength of regular Delta 9 THC.
Then, in 1978, in Jacksonville, Florida, there was another attempt to produce THC-O as a form of a concentrated cannabis extract. This included acetylation with acetic anhydride.
- 12 strain specific terpene flavors + unflavored
- From $0.003 per MG THCO
- DIY fill a 1g cart for $3.33!
- Third party tested
THC-O Effects: The Spiritual Cannabinoid That Will Take You To Space
Most users’ reports highlight that the effects lean much more towards the psychedelic side of the spectrum. With this cannabinoid, there is a tendency for deep introspection.
Ultimately, THC-O is highly psychoactive.
If consumed, it should be taken with caution as it probably carries a higher likelihood of side effects that could linger for a while.
When vaped or dabbed, the THC-O distillate is said to have an initial onset time of about 1 – 3 minutes. However, the effects may continue to increase for up to 1 hour following inhalation.
Currently, THC-O edibles are being developed. THC-O Acetate must be metabolized by the body before one can experience any effect. It’s pretty much the same case as with Delta 9 THC or CBD edibles.
With THC-O, the metabolizing should take between 30 – 60 minutes, depending on several factors. Developing edible options is important. Some people would benefit more from the cerebral high of edibles.
In the meantime, others will prefer to stick to the more fast-acting effect of smoking or dabbing.
THC-O VS Delta 8, 9 & 10: 3 Times More Potent!
Keeping things short and straight to the point here.
THC-O is very, VERY potent (yup, mind the Caps Lock, it’s indeed potent!).
It’s 3x more potent than Delta 9 THC. So much stronger than Delta 8 and 10, too. Although, it’s not quite as psychoactive as THCP.
Is THC-O Legal?
Similar to Delta 8 THC and Delta 10 THC, the legality of THC-O is a gray area. Therefore, it is not scheduled at the federal level…Yet anyway.
Yes, it’s an analog of THC. But as it is derived from hemp, THC-O falls into a grey zone; based on the 2018 Farm Bill.
Legality aside, there are other challenges related to the evolving THC-O market. It’s still hard to define the potency levels of the compound. The thing is, most labs aren’t testing for it.
THC-O Products: The Upcoming THC-O Market Boom
THC-O is such a new substance that there are few products on the market today. There is still little to no research available on the long-term effects of THC-O.
It will take much more time before we know for sure how this compound affects the human body in the long run.
Right now, you can mostly find THC-O vape cartridges. But it’s likely that, as with Delta 9 and Delta 10, you’ll soon find a whole array of products.
Yup, THC-O gummies, capsules, tinctures, and so much more are on their way.
Meanwhile, it sounds like THC-O is also nano-encapsulated by Honest Marijuana Company using a patented technology called Nanobidiol.
The goal is to make it water-soluble and widely sold in dispensaries.
In an article published by Cannabis Tech, Serge Chistov, the inventor of Nanobidiol technology, shares valuable information.
He explains the need for well-acting THC-O acetate-infused edibles. The goal is more of an energetic rather than a sedative high.
“I might want to eat a gummy and go skiing, but after eating the gummy, I’m suddenly more interested in Netflix and ice cream.”
In another article published by Extraction Magazine, Chistov shares:
“Using Nanobidiol as a delivery technology, we’re able to fill any cannabinoid in the capsule and make that cannabinoid more active and bioavailable.”
Both THC and CBD, among other cannabinoids, are not water-soluble. Instead, they need to bind with fats to dissolve. Once dissolved, we can feel stronger effects.
But due to the poor bioavailability, a huge amount of cannabinoids’ potency is lost. The human body is only able to intake a certain amount, and the rest is pretty much lost. Water-soluble products aim to solve this and offer maximized potency.
Of course, all methods used must only take advantage of safe extraction chemicals. This way, the final product should not pose health risks to users.
Related Read: THCO Compared To HHC
At Departure: Some Canna-Knowledge Food For Thought
The continuously evolving methods for extracting cannabinoids and essential oils from the cannabis plant are changing the world.
The cannabis industry is on a quest for improved potency and bioavailability. Newfound cannabis compounds could help in our quest for alternative therapies.
Pharmaceutical-grade cannabinoid extracts can be life-changing for some people. With treatment resistance becoming more commonplace, understanding the potential benefits and risks of compounds like THO and other related THC products is quintessential.
Thus, laboratory processes that lead to something different than what we know so far must not be condemned. These laboratory processes are pathways to studying and improving cannabinoid expression.
The big question in front of the cannabis community:
Will we choose to educate ourselves about the ongoing development of new cannabis products?
That’s what makes the difference between insatiable consumers and conscious green plant users.



